What Are Dental Sealants?
Sealants/PRRs
What are dental sealants?
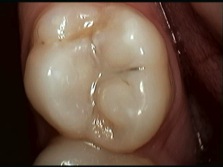
Many of the permanent teeth develop with very deep grooves. These grooves are difficult to clean and are prone to decay. Dental sealants are thin protective coatings that are applied to the grooves to protect them from tooth decay. Most tooth decay in children and teens occurs on the chewing surfaces. Sealants protect the chewing surfaces from tooth decay by keeping germs and food particles out of these grooves.
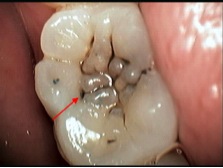
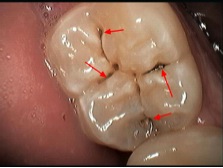
Why are sealants important?
Decay damages teeth permanently. Sealants provide an easy and cost effective way to prevent dental decay.
What age is suitable for my child to have sealants?
Permanent molars are the most likely to benefit from sealants. The first molars usually come into the mouth when a child is about 6 years old. Second molars appear at about age 12. It is best if the sealant is applied soon after the teeth have erupted, before they have a chance to decay.
How long will sealants last?
A sealant can last for many years. Sealants should be checked at your regular dental appointment and can be reapplied if they are no longer in place.
What is a preventive resin restoration (PRR)?
A preventive resin restoration is a more definitive treatment for sealing teeth if early decay has already started in the grooves. This procedure involves cleaning out the grooves rather than just sealing the surface. The grooves are generally cleaned out with a conventional drill. Once the grooves have been cleaned out they are filled with white filling (resin) material. If the decay has spread deeper then the grooves then a conventional filling is required.
How do sealants/PRRs fit into a preventive dentistry program?
Sealants/PRRs are one part of a child’s total preventive dental care. A complete preventive dental program also includes fluoride, twice-daily brushing, wise food choices, and regular dental care.